
Understanding Test and United States Prices: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to comparing prices in the United States, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of the factors that influence them. In this article, we will delve into the concept of “test” and how it relates to pricing in the United States. We will explore various dimensions, including market dynamics, consumer behavior, and economic indicators, to provide you with a comprehensive overview.
What is “Test”?
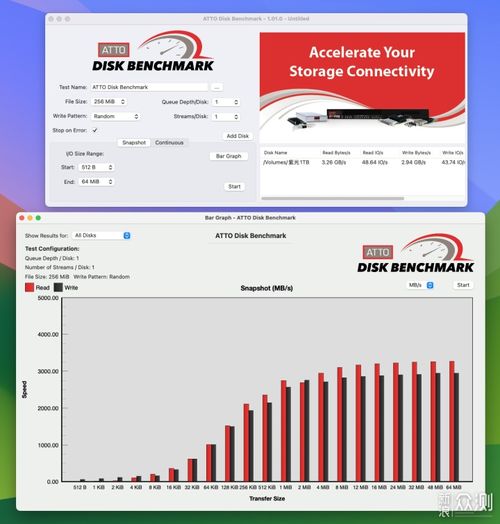
“Test” refers to the process of evaluating a product or service to determine its quality, performance, or suitability for a particular purpose. In the context of pricing, “test” can be seen as a trial period during which a product or service is offered at a discounted rate to gather feedback and assess market demand. This section will discuss the significance of testing in the pricing strategy of products and services in the United States.
Testing is a crucial step in the product development process. It allows companies to identify potential issues, refine their offerings, and make informed decisions about pricing. By offering a product or service at a lower price during the testing phase, companies can attract a larger customer base and gather valuable insights into consumer preferences and market trends.
Market Dynamics
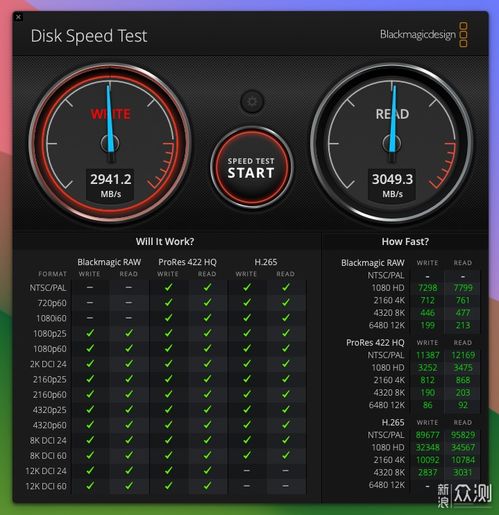
Understanding market dynamics is essential when analyzing prices in the United States. The following table provides a snapshot of the key factors that influence pricing in the country:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Supply and Demand | The relationship between the availability of goods and services and the desire of consumers to purchase them. |
| Competition | The level of competition within a market, which can affect pricing strategies. |
| Economic Indicators | Statistics that reflect the overall health of the economy, such as GDP, inflation, and unemployment rates. |
| Consumer Behavior | The preferences, habits, and purchasing patterns of consumers. |
Supply and demand play a significant role in determining prices. When demand exceeds supply, prices tend to rise, and vice versa. Competition also influences pricing, as companies may adjust their prices to stay competitive in the market. Economic indicators, such as inflation and unemployment rates, can impact consumer spending power and, consequently, pricing.
Consumer Behavior

Consumer behavior is a critical factor in understanding pricing in the United States. The following table outlines some key aspects of consumer behavior that affect pricing:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | The degree to which consumers are sensitive to changes in price. |
| Brand Loyalty | The tendency of consumers to remain loyal to a particular brand. |
| Value Perception | Consumers’ perception of the value they receive from a product or service. |
| Demographic Factors | Characteristics such as age, income, and education level that influence consumer behavior. |
Price sensitivity varies among consumers, with some being more willing to pay a premium for quality or convenience. Brand loyalty can also impact pricing, as consumers may be willing to pay more for a trusted brand. Value perception plays a crucial role in determining whether consumers believe a product or service is worth the price. Additionally, demographic factors can influence pricing strategies, as different consumer segments may have varying preferences and purchasing power.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators provide insights into the overall health of the economy and can influence pricing in the United States. The following table lists some key economic indicators and their potential impact on pricing:
| Indicator | Description | Impact on Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | The total value of all goods and services produced within a country over a specific
|

















